Mitsubishi Electric Advances Automation and Robotics with MELFA RV-CR and RH-CRH Series
As global robot installations hit record highs, Mitsubishi Electric’s latest robotic innovations tackle key industry challenges—offering compact, low-maintenance, and no-code solutions for smarter, scalable automation across manufacturing sectors.
Image Courtesy: Public Domain
The global manufacturing landscape is increasingly embracing robotics, as evidenced by a substantial rise in installations worldwide. According to the World Robotics 2024 Report, over 4.28 million robots are now operating in factories, marking a 10% increase, with annual installations surpassing half a million units for the third consecutive year.
This trend reflects not only a growing reliance on robotics to enhance production capabilities but also demonstrates that companies are effectively overcoming key implementation challenges associated with robotics integration.
Robotics at Its Momentum
The European market for industrial robots exemplifies this growth, with installations climbing 9% to a record 92,393 units in 2023. Germany, as the largest European market, saw a 7% increase to 28,355 units, while the UK experienced a robust 51% growth, reaching 3,830 units, primarily fueled by investments in the automotive industry. While specific data for 2024 installations is not yet available, the International Federation of Robotics forecasts continued high adoption with approximately 82,000 units. Looking ahead, global robot installations are expected to trend sideways at 541,000 units, with accelerated growth anticipated from 2025 through 2027. The long-term growth trend shows no signs of slowing down anytime soon.
This momentum indicates that manufacturers are successfully navigating the complexities of robotic implementation to improve efficiency and productivity.
"We're seeing more widespread adoption of robotics technology," says Oliver Giertz at Mitsubishi Electric. "Manufacturing facilities of various sizes are integrating robots into their operations. Our MELFA RV-CR and RH-CRH series are designed to be cost-effective options for both large corporations and smaller manufacturers. This broader accessibility contributes to the growth in global robot installations we're observing."
No-Code Programming
Despite the surge in robotic adoption, manufacturers continue to face challenges, particularly the skills gap in automation technology. According to the McKinsey Global Industrial Robotics Survey, 61% of companies cite lack of experience with automation as a barrier. In addition, 30% of manufacturers identify difficulties in attracting and retaining skilled workers as a top concern for 2025.
The MELFA RV-CR and RH-CRH series robots use the CR800 controller system with visual programming that allows users to connect functional blocks representing specific commands. This approach can help staff without specialized robotics training to use the system. The MELSOFT RT ToolBox3 software allows users to simulate programs before implementation, reducing the need for expert programmers.
Solving Integration Hurdles
A recent SYSPRO study reveals that 30% of manufacturers struggle with integrating new technologies into existing systems. “The MELFA RV-CR and RH-CRH series have features that address these integration challenges. Their compact designs can help optimise workspace utilisation in various production environments. Built-in signal wiring and air piping reduces the need for external cabling” - adds Olivier Gierz, Strategic Product Manager for Servo & Robots at Mitsubishi Electric at Mitsubishi Electric.
The robots can perform tasks such as picking, packing, sorting, and quality assurance across sectors including automotive component handling, laboratory work, machine building, quality control inspections, and assembly operations.
The CR800 controller includes functions such as simultaneous control of additional axes and conveyor tracking. Integration with Mitsubishi Electric's new R86TB teaching box, which serves as an interface for robot setup, programming and maintenance, enhances the user experience throughout the robot's lifecycle. The R86TB features a 10.1" display for accessing control screens and includes 3D visualization tools for programming robotic tasks. The teaching box is compatible with both new and previous generations of MELFA robots, offering functionality for parameter input, diagnostics, and programming without requiring a separate computer
Both series use battery-less servo motor technology, eliminating the need for periodic battery replacements and reducing the risk of position loss due to battery failures. The beltless coaxial drive mechanism means fewer points requiring periodic belt inspections. The lighter weight and heat dissipation characteristics can benefit extended operation periods.
Two Series for Various Applications
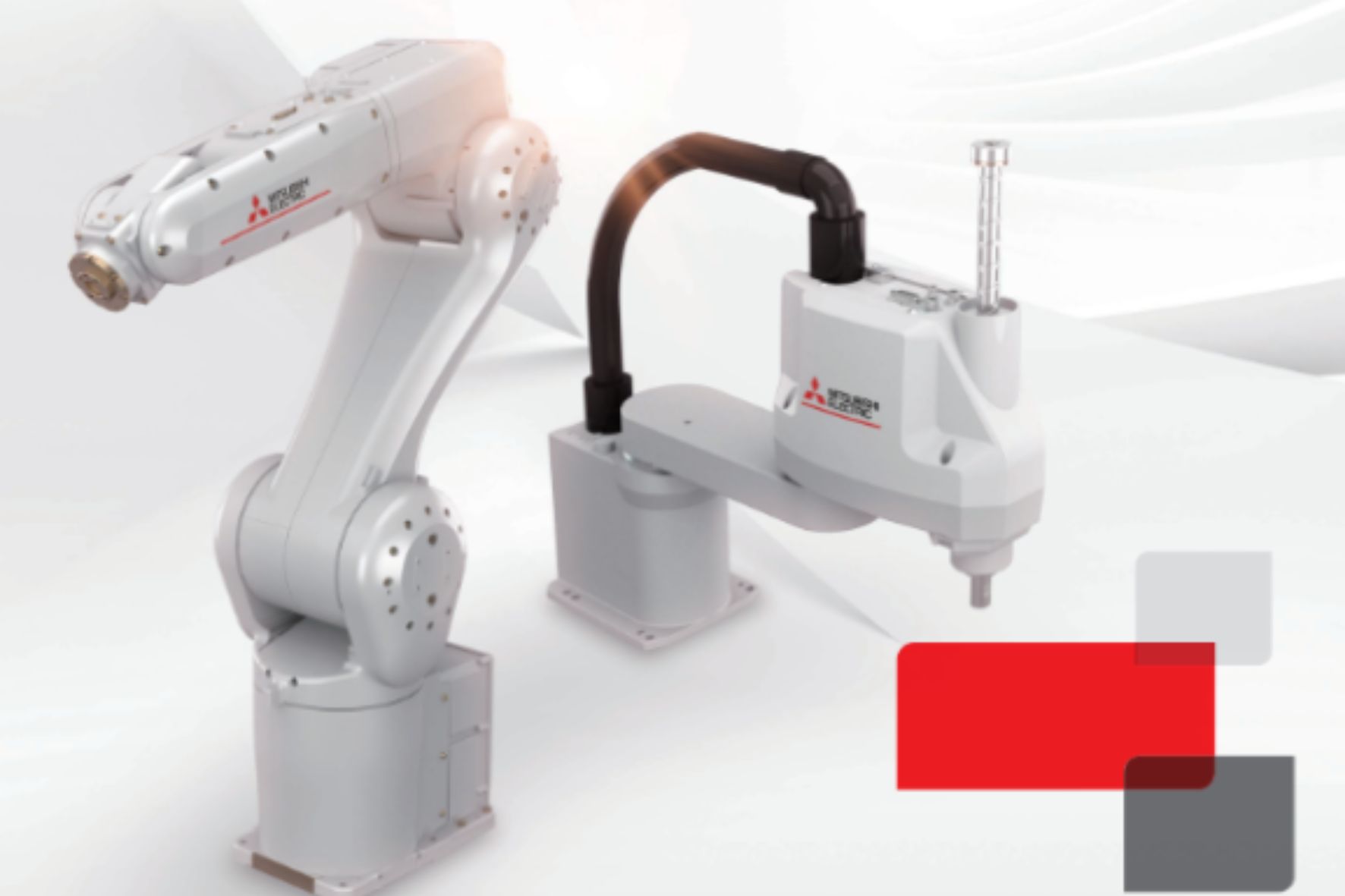
Mitsubishi Electric has introduced two robot series for manufacturing environments. The MELFA RV-CR series consists of vertical articulated robots with payloads suitable for industrial applications. These robots feature compact footprints and reduced maintenance requirements.
The MELFA RH-CRH series comprises SCARA robots with designs that offer 65% reduction in height and 50% reduction in weight compared to previous FR series models. This series provides automation capabilities with quick cycle times and standard network connectivity, making them suitable for space-constrained environments.
Industry Compatibility
Both the MELFA RV-CR and RH-CRH series work with Mitsubishi Electric's e-F@ctory concept and can integrate with networks like those supported by the CC-Link Partners Association (CLPA). This compatibility allows companies to incorporate these robots into their existing manufacturing infrastructure.
The MELFA RV-CR series features minimal protrusions, which reduces interference with surroundings during operation. The MELFA RH-CRH series offers space-saving benefits with its reduced height and footprint. Both robot series use a beltless coaxial drive mechanism that may require less maintenance.
The MELFA RV-CR and RH-CRH series include visual programming, battery-less motor technology, compact design, built-in wiring and piping, and controller functions that support different manufacturing applications. These robots are designed to address various manufacturing needs.